Regarding this, what does the Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act do?
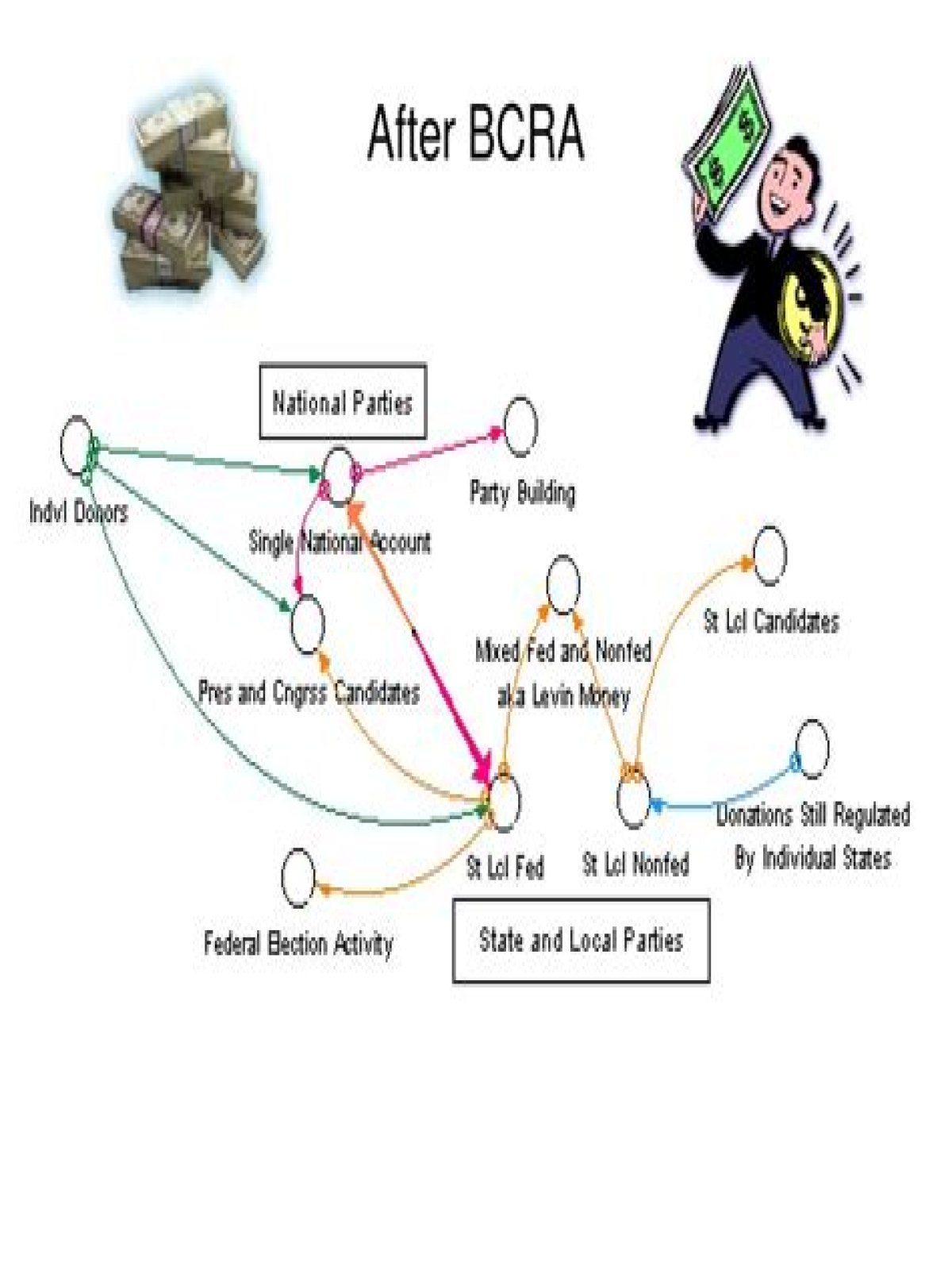
The BCRA decreased the role of soft money in political campaigns as the law places limits on the contributions by interest groups and national political parties.
Likewise, what two parts of the BCRA were upheld? Case Summary. On December 10, 2003, the Supreme Court issued a ruling upholding the two principal features of the Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act of 2002 (BCRA): the control of soft money and the regulation of electioneering communications.
Correspondingly, how did the Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act 2002 change campaign finance in the United States?
The Bipartisan Campaign Reform Act (BCRA) of 2002, also known as "McCain-Feingold", after its sponsors, is the most recent major federal law on campaign finance, the key provisions of which prohibited unregulated contributions (commonly referred to as "soft money") to national political parties and limited the use of
What were the main provisions of the McCain Feingold Act?
Its key provisions were 1) a ban on unrestricted ("soft money") donations made directly to political parties (often by corporations, unions, or wealthy individuals) and on the solicitation of those donations by elected officials; 2) limits on the advertising that unions, corporations, and non-profit organizations can