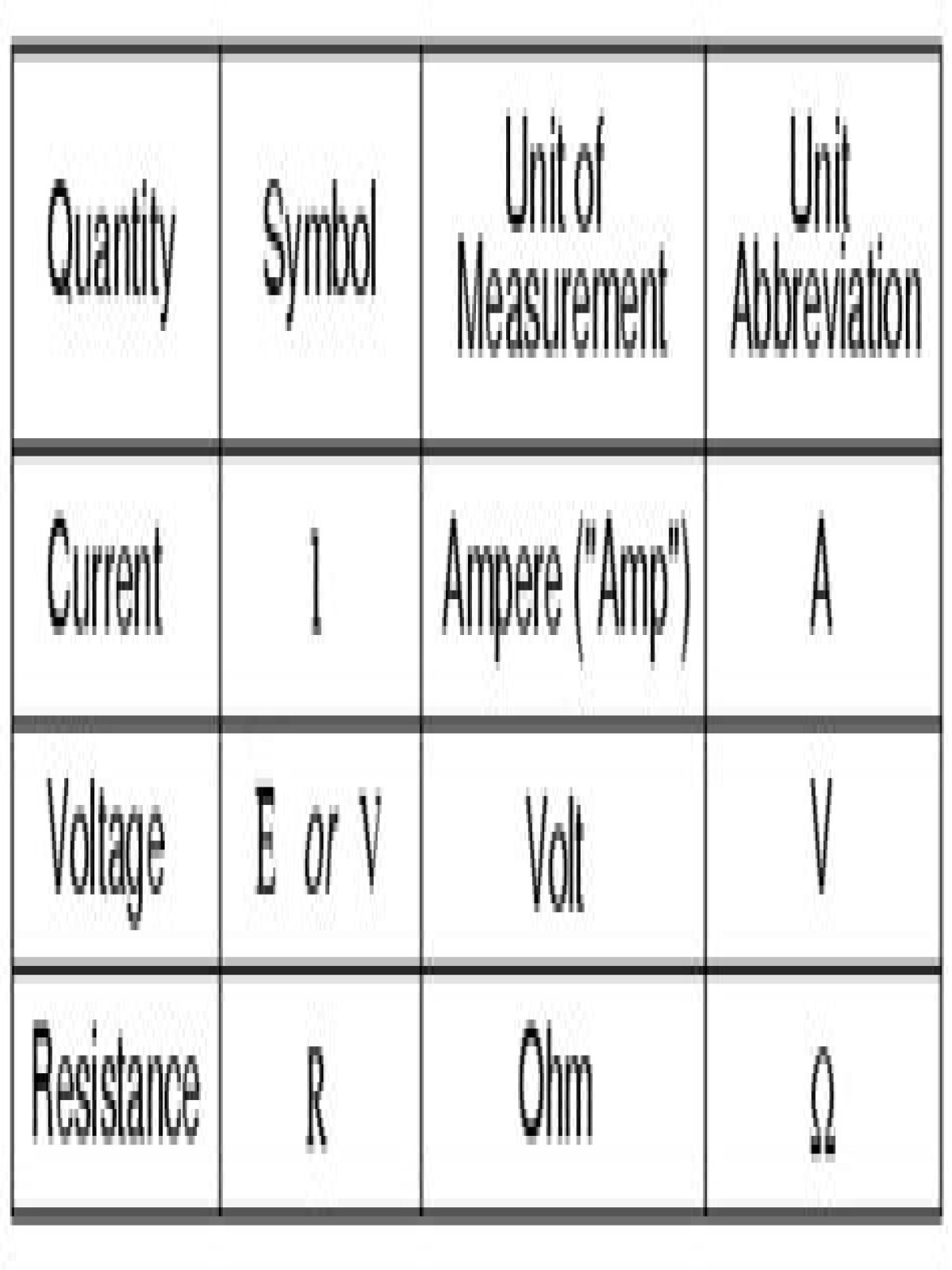
| Unit Name | Unit Symbol | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Ampere (amp) | A | Electric current (I) |
| Volt | V | Voltage (V, E) Electromotive force (E) Potential difference (Δφ) |
| Ohm | Ω | Resistance (R) |
| Watt | W | Electric power (P) |
Similarly, what is the unit for voltage?
The unit of potential difference is Volt (V) which is also equal to Joule per Coulomb (J/C). The SI unit for voltage is Volt and is represented by the letter v. volt is a derived SI unit of electromotive force or electric potential.
Furthermore, which symbol and unit of measurement are used for voltage? V
Herein, how do we measure voltage and what is the unit of voltage?
In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named volt. In SI units, work per unit charge is expressed as joules per coulomb, where 1 volt = 1 joule (of work) per 1 coulomb (of charge).
How do you measure voltage?
Voltage is a measurement of potential electric energy between two points. You can measure the voltage of household circuitry or batteries using a digital multimeter, an analog multimeter, or a voltmeter. Most electricians and novices prefer a digital multimeter, but you can also use an analog multimeter.