In respect to this, is blood only in your veins?
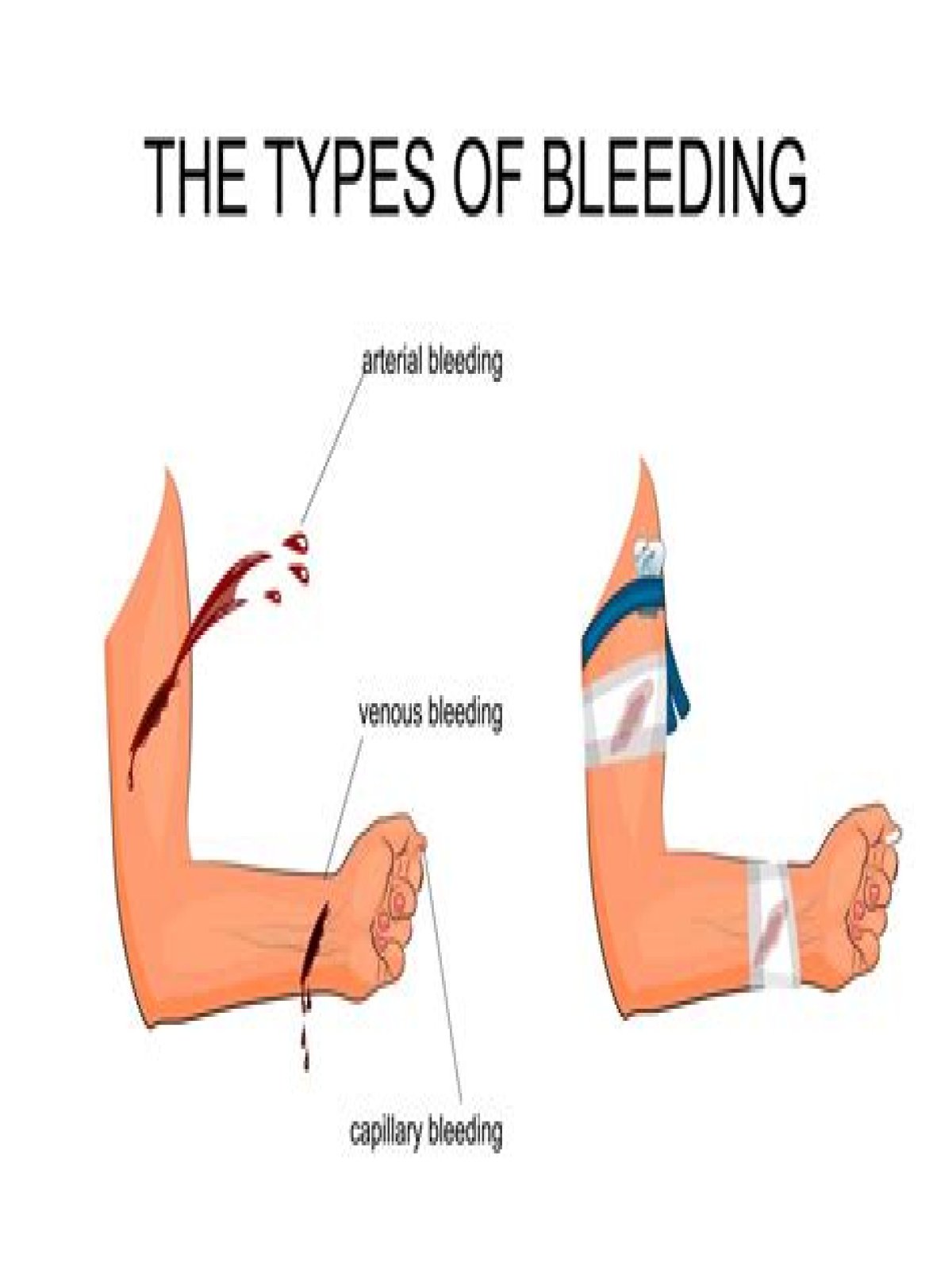
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Furthermore, what happens when there is no blood flow to the legs? Peripheral artery disease (PAD) can lead to poor circulation in your legs. In an associated condition called atherosclerosis, arteries stiffen due to plaque buildup in the arteries and blood vessels. Both conditions decrease blood flow to your extremities and can result in pain.
Also know, what happens if a vein is blocked?
A clot blocks blood circulation through these veins, which carry blood from the lower body back to the heart. The blockage can cause acute pain, swelling, or warmth in the affected leg. Blood clots in the veins can cause inflammation (irritation) called thrombophlebitis.
How do you anchor a vein?
Anchor the vein by holding the patient's arm and placing a thumb BELOW the venepuncture site. Ask the patient to form a fist so the veins are more prominent. Enter the vein swiftly at a 30 degree angle or less, and continue to introduce the needle along the vein at the easiest angle of entry.