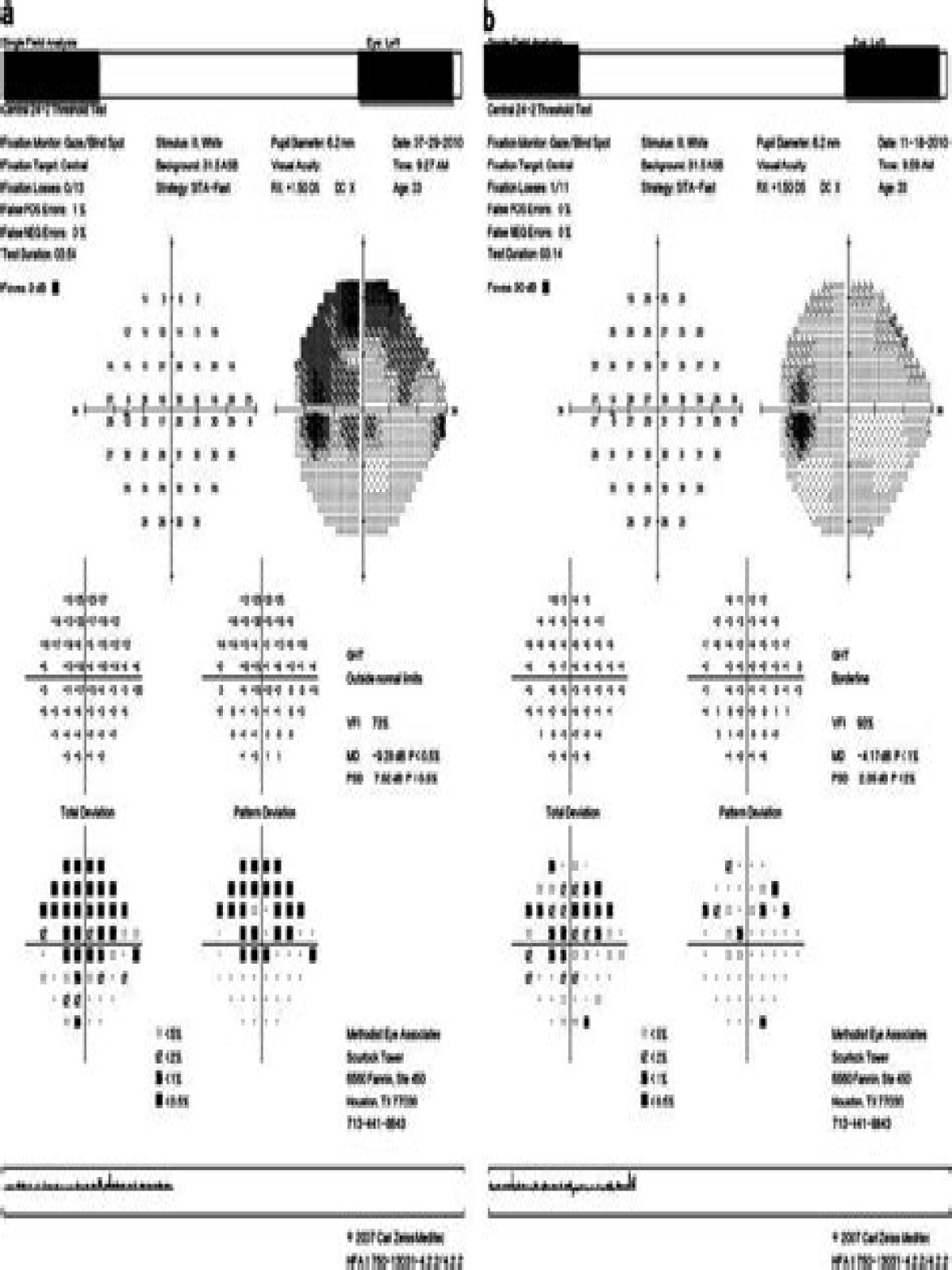
Keeping this in view, what is an arcuate visual field defect?
Glaucomatous damage to a nerve fiber bundle containing axons from both the inferonasal and inferotemporal retina resulted in the arcuate defect shown. The scotoma often begins as a single area of relative loss, which then becomes larger, deeper, and multifocal.
Similarly, what does it mean if you have large optic nerves? The cupping of the optic nerve means the size of the depression in the middle of the nerve when viewed from the front of the eye. When a person is shown to have large optic nerve cups, it could be an indicator of damage unless it can be determined that the cup size is considered normal for that individual.
In this way, what causes a scotoma?
A scotoma is caused by a problem in your brain, a problem in your eye, or a problem in your optic nerve. The optic nerve is located behind your eye and sends pictures to the brain. The kinds of problems that can cause a scotoma include: A stroke.
Can scotoma be cured?
Unfortunately, scotomas cannot be corrected by glasses or contact lenses. Sometimes surgery may be helpful in treatment of a scotoma. For example, if the scotoma is caused by a tumor, removal of the tumor may correct the scotoma.
How fast does glaucoma progress?
What can be mistaken for glaucoma?
Can an optometrist detect glaucoma?
What makes you a glaucoma suspect?
What is the first sign of glaucoma?
Can you have glaucoma in just one eye?
Can anemia cause glaucoma?
What is Bjerrum scotoma?
Are Scotomas dangerous?
Do Scotomas get worse?
How long does scotoma last?
How is scotoma diagnosis?
Do Scotomas move?
What does the blind spot look like?
Can stress cause an aura?
How do u know if ur going blind?
- A sudden onset of many spots and floaters in your field of vision.
- A sensation that a dark curtain has settled across your field of view.
- Sudden eye pain, redness, nausea and vomiting.
- Sudden blind spot in one eye.
- Poor night vision, halos around lights or less vivid color vision.