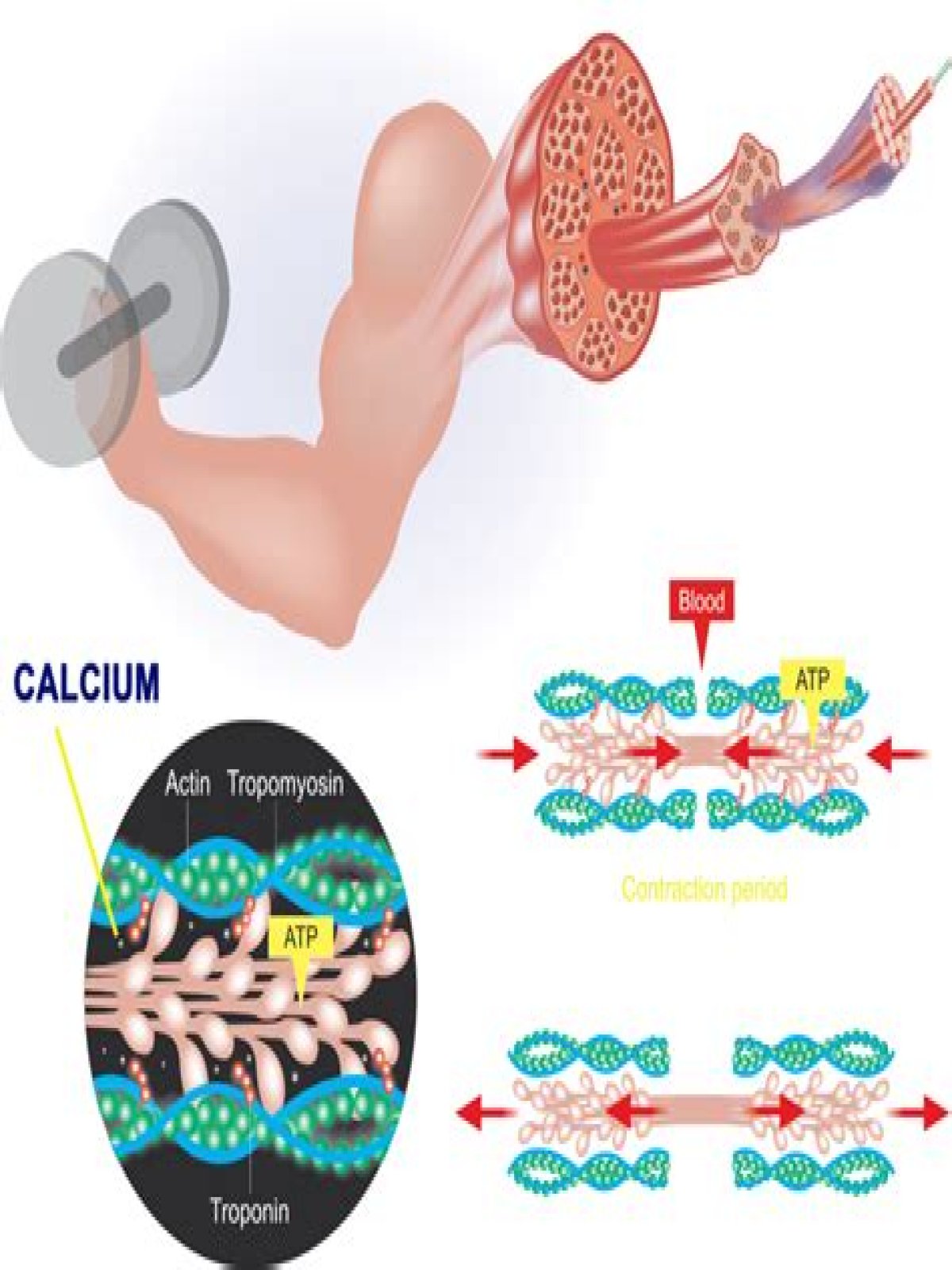
Similarly, you may ask, how does calcium affect muscle contraction?
The muscle contraction cycle is triggered by calcium ions binding to the protein complex troponin, exposing the active-binding sites on the actin. ATP can then attach to myosin, which allows the cross-bridge cycle to start again; further muscle contraction can occur.
Also Know, why is calcium necessary for muscle contraction quizlet? Calcium is needed to allow the muscle fiber to become depolarized. Calcium is needed to activate troponin so that tropomyosin can be moved to expose the myosin-binding sites on the actin filament. Calcium functions as a neurotransmitter and is released from the motor neuron.
One may also ask, can a muscle contract without calcium?
Without calcium, TROPONIN returns to its original shape and position as does the attached TROPOMYOSIN. This means that TROPOMYOSIN is now back in position, in contact with the MYOSIN HEAD. So, the MYOSIN head is no longer in contact with ACTIN and, therefore, the muscle stops contracting (i.e., relaxes).
What would happen to a muscle contraction If there was an excess amount of calcium?
In MH an acute increase of Ca2+ results in excessive muscle contraction causing rigidity, while in CCD a chronic rise of cytosolic Ca2+ is seen, leading to mitochondrial damage, disorganization of myofibrils and muscle weakness.
What is the importance of calcium in muscle contraction?
Why is muscle contraction important?
What is skeletal muscle contraction?
How does muscle contraction occur?
Does calcium affect muscles?
What is the source of calcium for skeletal muscle contraction?
Does calcium relax muscles?
What is tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
What is the source of energy for muscle contraction?
Where is calcium stored in the muscle?
How does ATP supply energy for muscle contraction?
What are the 4 types of muscle contractions?
- Isometric. If I hold the weight still, the muscle is engaged but doesn't change length.
- Concentric. When I bring that weight towards my shoulder, the biceps muscle shortens.
- ECCENTRIC. As I lower the weight, the biceps lengthens.